What:
- Apache Phoenix is sql skin over No Sql database (HBase).
- Its Enables OLTP and operational analytics on Hbase.
- Apache Phoenix is fully integrated with other Hadoop products such as Spark, Hive, Pig,Flume, and Map Reduce.
Who/When:
- The project was created by the Salesforce.
- It was originally open-sourced on GitHub and became a top-level Apache project on 22 May 2014.
Challenge
:
- The challenge today is blending the scale and performance of NoSQL with the ease of use of SQL
Hbase
- •Hbase NoSQL column family database
- •Store data as sorted maps as byte Array
- •Low level APIs
- •Write Java code or use low level API
Why Phoenix
- Relational database engine supporting OLTP for Hadoop use Apache Hbase as its backing store.
- Transforms SQL queries to Hbase calls hence hiding complexities for noSQL functions.
- Low Latency
- Reduces the amount of code users need to write
- Performance optimizations transparent to the user(scans, server-side filter, secondary indexes )
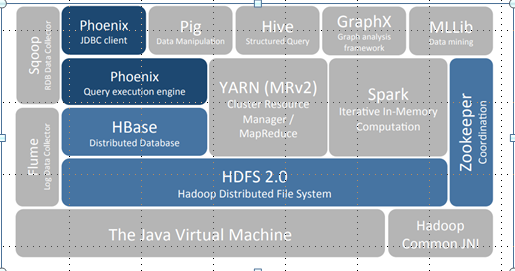
Phoenix and Hbase together
Accessing HBase data
with Phoenix can be easier than direct HBase API
SELECT
column
FROM
table
WHERE column >
30
Versus
scan 'table', {FILTER => "ValueFilter(=,'binary:30')",LIMIT => 10}
HTable t =
new HTable(“table”);
RegionScanner s = t.getScanner(new
Scan(…, new ValueFilter(CompareOp.GT,
new CustomTypedComparator(30)),…));
while ((Result r = s.next())
!= null)
{
//
Reading values from Result class object
byte []
value = result.getValue(Bytes.toBytes(“columnfamily"),Bytes.toBytes("
column "));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(value));
}
s.close();
Architecture
•Phoenix
pushes processing to the server - most "by hand” API accesses do not use co-processors
•Phoenix
supports and uses secondary indexes
•Phoenix
uses "every trick in the book" based on various factors: the HBase
version, metadata and query, reverse scans, small scans, skip scans, etc.
Few Phoenix SQLs:
Create table -
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS us_zip (
zip CHAR(5) NOT NULL,
city VARCHAR NOT NULL,
hhc
BIGINT
CONSTRAINT my_pk
PRIMARY KEY (zip,city))
DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING='NONE',VERSIONS=5,MAX_FILESIZE=2000000
split on (‘a’, ‘p’ ,’r)’
COMPRESSION=‘LZ4’
TRANSCATIONAL=true;
Insert few records -
UPSERT INTO us_zip VALUES('60500','New York', 81431);
UPSERT INTO us_zip VALUES('60501',‘Dallas', 91233);
UPSERT INTO us_zip VALUES(‘06095,‘Windsor, 92433);
Query -
SELECT zip,city ,hhc
FROM us_zip
where hhc =
(select max(hhc)
from us_zip );
View on the top of Hbase
table -
CREATE VIEW “test_log“
( k VARCHAR primary key, “name”."value"
VARCHAR);
CREATE VIEW my_view ( new_col
SMALLINT )
AS SELECT * FROM my_table
WHERE k = 100;
Phoenix
benefits
•SQL
Datatypes built in
•Schemas,
DDL, Hbase
Properties
•Composite
Primary Key
•Map
existing Hbase
tables
•Write
to Hbase,
read from Phoenix
•Salting
•Indexes
•Client side rewriting
•Master-slave
configuration
•Parallel scanning with final client
side merge sort
•RPC batching
•Use secondary indexes if available
•Rewrites for multitenant tables
•Server side push down
•Filters
•Skip scans
•Parallel Aggregation
•TopN
(coprocessor)
•Join
and Subqueries
•Inner,
left, right, Full Outer join, Cross Join, Semi Join, Anti Join
•Query
server – Similar to REST Server
•Protobuf 3.0 over http
•Has
JDBC thin client
•Spark
Integration
•Secondary
index
•At query time, the optimizer will
use the index if it contains all columns referenced in the query and produces
the most efficient execution plan
•Global index
•CREATE
INDEX my_idx ON sales.opportunity(last_updated_date
DESC)
•Read
optimized(Use case)
•Different
table per index
•Transactional
tables indexes have ACID guarantee
•Local Index
•CREATE
LOCAL INDEX my_index ON my_table (v1)
•Write
optimized (Use case)
•Use
same table – different CF
•Functional index
•Supported
By default, unless hinted, an index
will not be used for a query that references a column that isn’t part of the
index.
Future Road map
•Calcite Support
•No Generic Yarn or Tez
layer
•Offset support
•Local index re-implementation





Your company is one of the data migration solutions providers , which had helped in integrating useful data for business purposes. Applications designing, as well as the correct solutions of data migration, are helpful for accurate loading data.
ReplyDeleteThe article is so appealing. You should read this article before choosing the Google cloud big data services you want to learn.
ReplyDelete